DMP Last update:
You need to know the platform better, we invite you to consult our documentation.
Register
To register, go to the home page and click the register button. Fill in the requested information and choose its category among the categories listed below. The category 'Hospitals' includes clinics, health centers and medical offices; the catogory 'Pharmacy' includes parapharmacies. Once the registration is completed, you will receive a confirmation email; if the email is not received within minutes of your registration, consult your spam and if still nothing: send and email to contact@smartcare.fr.
Dashboard
The dashboard gives an overview of the account through graphs and/or tables. Its content changes depending on the account category :
- Hospitals: Appointment
- Doctors: Appointment
- Pharmacy: Appointment
- Laboratory: Appointment
- Patient: Appointment, arterial pressure, body mass, size, blood sugar, insulin, temperature, ...
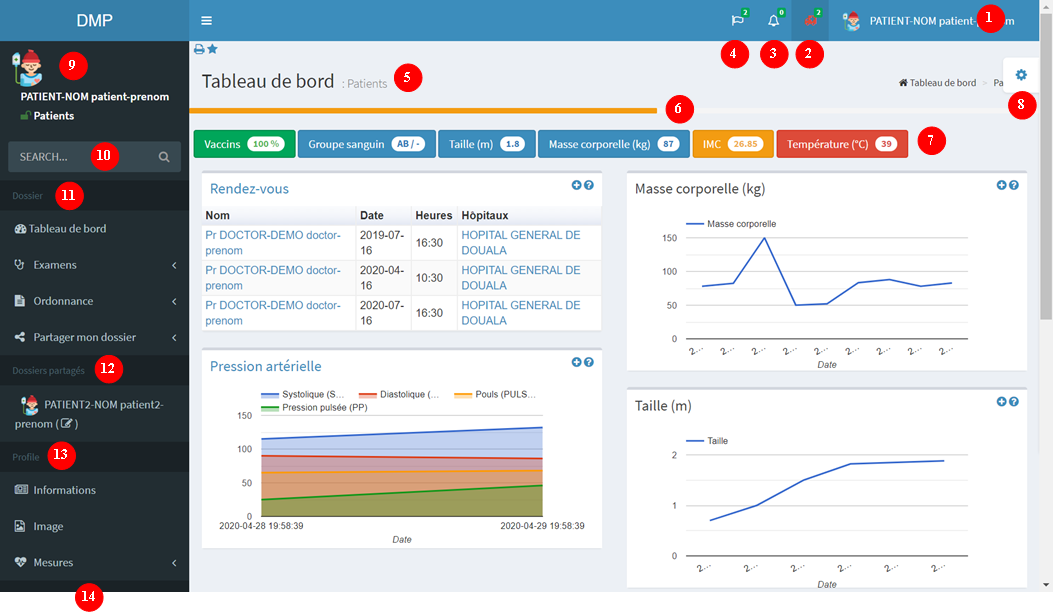
- 1: User connected : this is a menu with several options.
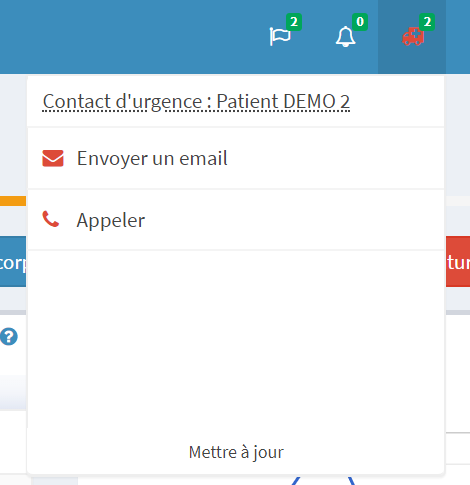
- 2: Access emergency contact
- 3: Notifications : Stay informed about events (appointments, exam results,...)
- 4: Languages : select the console display language. To set a default language you need to change it in your information.
- 5: Current page : display of the content of the selected page
- 6: Profile : Profile fill level. Ideally it should be green
- 7: Badges : Display important information and change according to the category (patient, doctor, hospital...) of the user.
- 8: Options : Change the display settings (color, bar,...)
- 9: Ongoing consultation : It corresponds to the logged-in user for all categories except for patients and doctors. For these two specific cases, it corresponds to the medical record being consulted. For more information Shared record
- 10: Search bar: search in your folder. The result depends on the category
- 11: Interaction with patient's folder. Buttons depends on the category and folder access rights.
- 12: List of shared folders i was given access to
- 13: Profile: section dedicated to profile editing.
- 14: Documentation: link to this page
Profile
Profile
It is recommended to have a profile completed at least 60%.
Exams
...
Drugs
You must respect the dosage and method of administration provided by your doctor.
Statut:
Emergency contact
We advise you to define an emergency contact. The latter will be contacted in case of emergency : accident, hospitalization, ... death . It consists of a name, phone number and email and is on the patient' emergency card. For this purpose, we advise you to download a new card when updating your information.
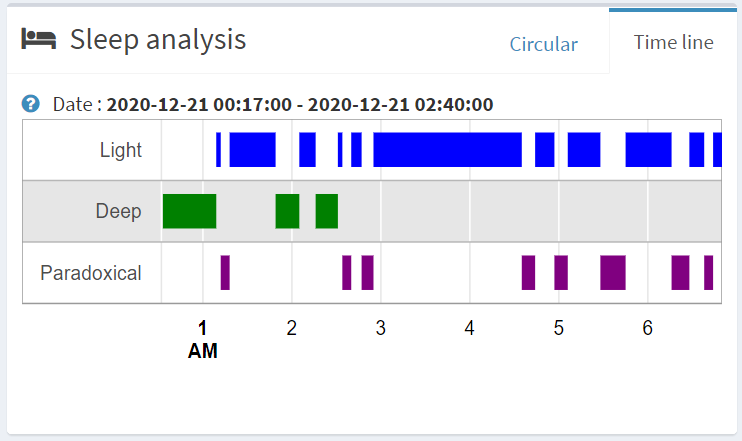
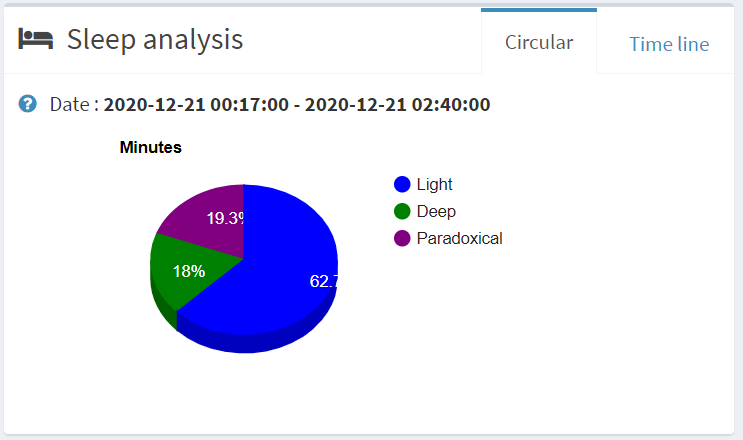
Time line
The timelines allow you to see your consultations, prescriptions, ... with a distribution over time.
Shared folder
All your data is private and confidential but for consultation or support purposes, you have the option to share your folder with a docteur (writing) or with a relative (Reading or writing). To do this you have to click the button Share my folder in your console and provide the person'ID. To get the ID you have to to go to information.
In addition to being able to define the access right (reading/writing), you have the option to set a duration in days or unlimited.
If another user shares their folder with you, the user will be visible in your console in the section Shared folder. The latter displays the last 5 folder open. To view more, you have to click the all see button.
Vaccines
Find below the list of compulsory vaccines recommended by the WHO in general and the obligations by country.
| BCG | Universal BCG vaccination at birth is recommended in countries or settings with a high incidence of TB and/or high leprosy burden. A single dose of BCG vaccine should be given to all healthy neonates at birth, ideally together with Hepatitis B birth dose. | |
|---|---|---|
| Cholera | Appropriate case management, WaSH interventions, surveillance and community mobilization remain the cornerstones of cholera control. Vaccination should be implemented in relevant settings as part of comprehensive cholera control strategies or while other activities are being developed. | |
| DTP-containing vaccines | The need for early infant vaccination with DTP-containing vaccine (DTPCV) is principally to ensure rapid protection against pertussis, because severe disease and death from pertussis is almost entirely limited to the first weeks and months of life. | |
| Dengue (CYD-TDV) | Vaccination should be considered as part of an integrated dengue prevention and control strategy. Countries should consider introduction of the dengue vaccine CYD-TDV only if the minimization of risk among seronegative individuals can be assured. | |
| Haemophilus infuenzae type b | The use of Hib vaccines should be part of a comprehensive strategy to control pneumonia including exclusive breastfeeding for six months, hand washing with soap, improved water supply and sanitation, reduction of household air pollution, and improved case management at community and health facility levels. | |
| Hepatitis A | Hepatitis A vaccination is recommended for inclusion in the national immunization schedule for children ≥ 1 year if indicated on the basis of incidence of acute hepatitis A, change in the endemicity from high to intermediate, and consideration of cost-effectiveness. | |
| Hepatitis B | Hepatitis B vaccination is recommended for all children worldwide. Reaching all children with at least 3 doses of hepatitis B vaccine should be the standard for all national immunization programmes. Since perinatal or early postnatal transmission is the most important source of chronic HBV infection globally, all infants (including low birth weight and premature infants) should receive their first dose of hepatitis B vaccine as soon as possible after birth, ideally within 24 hours. | |
| Human Papillomavirus (HPV) | Recommended target population for the prevention of cervical cancer: females aged 9–14 years, prior to becoming sexually active. | |
| Japanese Encephalitis (JE) | JE vaccination should be integrated into national immunization schedules in all areas where JE is recognized as a public health priority. | |
| Measles | Reaching all children with 2 doses of measles vaccine should be the standard for all national immunization programmes. In addition to the first routine dose of MCV1, all countries should add a second routine dose of MCV2 to their national immunization schedules regardless of the level of MCV1 coverage. | |
| Meningococcal | Conjugate vaccines are preferred over polysaccharide vaccines due to their potential for herd protection and their increased immunogenicity, particularly in children < 2 years of age. | |
| Mumps | Recommended for use in high performing immunization programmes with the capacity to maintain coverage over 80% and where mumps reduction is a public health priority. | |
| Pneumococcal (Conjugate) | Currently available PCVs are safe and effective and are therefore recommended for the inclusion in childhood immunization programmes worldwide. | |
| Polio | In polio-endemic countries and in countries at high risk for importation and subsequent spread of poliovirus, WHO recommends a bOPV birth dose (zero dose) followed by a primary series of 3 bOPV doses and at least 1 IPV dose. | |
| Rabies | Production and use of nerve-tissue vaccines should be discontinued and replaced by vaccines based on RABV grown in cell culture or embryonated eggs (CCEEVs). There are two main immunization strategies for the prevention of human rabies: (i) PEP which includes extensive and thorough wound washing at the RABV-exposure site, together with RIG administration if indicated, and the administration of a course of several doses of rabies vaccine; (ii) PrEP which is the administration of several doses of rabies vaccine before exposure to RABV. PrEP is recommended for individuals at high risk of RABV exposure. These include sub-populations in highly endemic settings with limited access to timely and adequate PEP, individuals at occupational risk, and travellers who may be at risk of exposure. | |
| Rotavirus | Recommended to be included in all national immunization programmes. | |
| Rubella | All countries that have not yet introduced rubella vaccine, and are providing 2 doses of measles vaccine using routine immunization, or SIAs, or both, should consider including rubella containing vaccines (RCVs) in their immunization programme. Countries planning to introduce RCVs should review the epidemiology of rubella, including the susceptibility profile of the population; assess the burden of CRS; and establish rubella and CRS prevention as a public health priority. | |
| Seasonal Influenza (Inactivated Vaccine) | For countries considering the initiation or expansion of programmes for seasonal influenza vaccination, WHO recommends that pregnant women should have the highest priority. Children aged < 6 months are not eligible to receive currently licensed influenza vaccines and should be protected against influenza through vaccination of their mothers during pregnancy and through ensuring vaccination of close contacts. | |
| Tick-Borne Encephalitis (TBE) | Since the incidence of tick-borne encephalitis may vary considerably between and even within geographical regions, public immunization strategies should be based on risk assessments conducted at country, regional or district level, and they should be appropriate to the local endemic situation. Therefore, establishing case reporting of the disease is essential before deciding on the most appropriate preventive measures to be taken. | |
| Typhoid | Typhoid vaccination programmes should be implemented in the context of other efforts to control the disease, including health education, water quality and sanitation improvements, and training of health professionals in diagnosis and treatment. | |
| Varicella | Countries where varicella is an important public health burden could consider introducing varicella vaccination in the routine childhood immunization programme. However, resources should be sufficient to ensure reaching and sustaining vaccine coverage ≥ 80%. Decisionmaking on childhood varicella vaccination should also include consideration of the possible impact on herpes zoster. | |
| Yellow fever | WHO recommends that all endemic countries should introduce YF vaccine into their routine immunization programmes. A single dose of YF vaccine is sufficient to confer sustained life-long protective immunity against YF disease; a booster dose is not necessary. |